To monitor a remote Linux host using Nagios, we'll need to install Nagios Plugins and NRPE (Nagios Remote Plugin Executor) on the remote host.
NRPE (Nagios Remote Plugin Executor):
NRPE is a Nagios agent that allows remote systems to execute Nagios plugins on them. It facilitates the monitoring of local resources and services on remote hosts. NRPE can be installed on various operating systems, including Linux and Windows.
Here's a brief overview of how NRPE works:
- Nagios Server: The Nagios server initiates a check by sending a command to the NRPE daemon on the remote host.
- NRPE Daemon: The NRPE daemon on the remote host receives the command, executes the specified plugin locally, and returns the results to the Nagios server.
- Monitoring Plugins: Plugins are scripts or executables that perform specific checks (e.g., checking CPU usage, disk space, etc.) on the remote host.
- Secure Communication: NRPE uses encryption and authentication to ensure secure communication between the Nagios server and the remote host.
To monitor the remote Linux host we must install NRPE and Nagios Plugin,
here are the steps:
1. First let's check my Linux version
[root@src ~]# more /etc/*release;
::::::::::::::
/etc/oracle-release
::::::::::::::
Oracle Linux Server release 7.9[root@src ~]# more /etc/yum.repos.d/oracle-linux-ol7.repo
[ol7_latest]
name=Oracle Linux $releasever Latest ($basearch)
baseurl=file:///software/linux7
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-oracle
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
[root@src linux7]# yum update
2_2. Then install the following packages. [root@src linux7]# yum install -y gcc glibc glibc-common gd gd-devel make net-snmp openssl-devel tar wget2_3. Create Nagios user
[root@src linux7]# useradd nagios
[root@src linux7]# passwd nagios
Changing password for user nagios.
New password:
Retype new password:
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully. 2_4. Create directory for Nagios Plugin and download the package in this directory
[root@src linux7]# mkdir /root/nagios
[root@src linux7]# cd /root/nagios
[root@src linux7]# wget https://nagios-plugins.org/download/nagios-plugins-2.3.3.tar.gz3. Compile and install nagios plugin
[root@src nagios]# tar -xvf nagios-plugins-2.3.3.tar.gz
[root@src nagios]# ls -l
total 2724
drwxr-xr-x 15 root root 4096 Mar 11 2020 nagios-plugins-2.3.3
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2782610 Dec 15 16:36 nagios-plugins-2.3.3.tar.gz
[root@src nagios]# cd nagios-plugins-2.3.3
[root@src nagios-plugins-2.3.3]# ./configure
[root@src nagios-plugins-2.3.3]# make
[root@src nagios-plugins-2.3.3]# make install
##Set the permissions on the plugin directory using the chown command.
[root@src nagios-plugins-2.3.3]# chown nagios.nagios /usr/local/nagios
[root@src nagios-plugins-2.3.3]# chown -R nagios.nagios /usr/local/nagios/libexec
4. Install NRPE: Download the latest package, compile and install NRPE.
[root@src nagios]# cd /root/nagios
[root@src nagios]# wget https://github.com/NagiosEnterprises/nrpe/releases/download/nrpe-4.0.2/nrpe-4.0.2.tar.gz
[root@src nagios]# tar xzf nrpe-4.0.2.tar.gz
[root@src nagios]# cd nrpe-4.0.2
[root@src nrpe-4.0.2]# ./configure
[root@src nrpe-4.0.2]# make all
cd ./src/; make
make[1]: Entering directory `/root/nagios/nrpe-4.0.2/src'
gcc -g -O2 -I/usr/include/krb5 -DHAVE_CONFIG_H -I ../include -I ./../include -o nrpe ./nrpe.c ./utils.c ./acl.c -lssl -lcrypto -lnsl
gcc -g -O2 -I/usr/include/krb5 -DHAVE_CONFIG_H -I ../include -I ./../include -o check_nrpe ./check_nrpe.c ./utils.c -lssl -lcrypto -lnsl
make[1]: Leaving directory `/root/nagios/nrpe-4.0.2/src'
*** Compile finished ***
You can now continue with the installation or upgrade process.
Read the PDF documentation (docs/NRPE.pdf) for information on the next
steps you should take to complete the installation or upgrade.
[root@src nrpe-4.0.2]# make install-plugin
cd ./src/; make install-plugin
make[1]: Entering directory `/root/nagios/nrpe-4.0.2/src'
/usr/bin/install -c -m 755 -d /usr/local/nagios/bin
/usr/bin/install -c -m 755 ../uninstall /usr/local/nagios/bin/nrpe-uninstall
/usr/bin/install -c -m 775 -o nagios -g nagios -d /usr/local/nagios/libexec
/usr/bin/install -c -m 775 -o nagios -g nagios -d /usr/local/nagios/libexec
/usr/bin/install -c -m 775 -o nagios -g nagios check_nrpe /usr/local/nagios/libexec
make[1]: Leaving directory `/root/nagios/nrpe-4.0.2/src'
[root@src nrpe-4.0.2]# make install-daemon
cd ./src/; make install-daemon
make[1]: Entering directory `/root/nagios/nrpe-4.0.2/src'
/usr/bin/install -c -m 755 -d /usr/local/nagios/bin
/usr/bin/install -c -m 755 ../uninstall /usr/local/nagios/bin/nrpe-uninstall
/usr/bin/install -c -m 755 nrpe /usr/local/nagios/bin
/usr/bin/install -c -m 755 -o nagios -g nagios -d /usr/local/nagios/var
/usr/bin/install -c -m 755 -d /usr/lib/tmpfiles.d
/usr/bin/install -c -m 644 ../startup/tmpfile.conf /usr/lib/tmpfiles.d/nrpe.conf
make[1]: Leaving directory `/root/nagios/nrpe-4.0.2/src'
[root@src nrpe-4.0.2]# make install-config
/usr/bin/install -c -m 775 -o nagios -g nagios -d /usr/local/nagios/etc
/usr/bin/install -c -m 644 -o nagios -g nagios sample-config/nrpe.cfg /usr/local/nagios/etc
[root@src nrpe-4.0.2]# make install-init
/usr/bin/install -c -m 644 startup/default-service /usr/lib/systemd/system/nrpe.service
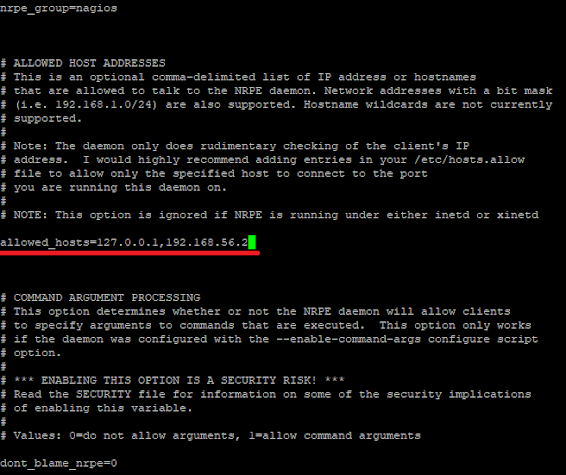
4_1. Now open /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg file and add the local host and IP address of the Nagios Monitoring Server.
[root@src nrpe-4.0.2]# vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg
allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1,192.168.56.24_2. Restart NRPE:
[root@src nrpe-4.0.2]# systemctl enable nrpe
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nrpe.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/nrpe.service.
[root@src nrpe-4.0.2]# systemctl restart nrpe4_3. Open NRPE Port in Firewall (I disabled the firewall in my Linux)
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=5666/tcp
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=5666/tcp --permanent[root@src nrpe-4.0.2]# systemctl status firewalld
● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: inactive (dead)
Docs: man:firewalld(1)[root@src nrpe-4.0.2]# netstat -na | grep "5666"
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5666 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 :::5666 :::* LISTEN
##verify the NRPE daemon is functioning properly by running the “check_nrpe” command that was installed earlier for testing purposes.
[root@src nrpe-4.0.2]# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 127.0.0.1
NRPE v4.0.2
Adding Remote Linux Host to Nagios Monitoring Server
we had installed NRPE On the Nagios Monitoring Server in the
previous article: Install Nagios Core on Oracle Linux 8.5 (OL8.5)
1. Verify NRPE Daemon Remotely
connect to the Nagios Server
# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H <remote_linux_ip_address>
[root@emcl libexec]# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 192.168.56.10
-bash: /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe: No such file or directory
# I checkedm, I the package source that I download for the Nagios server shit file was missing, therefore, I copied it from the remote host.
[root@emcl libexec]# ll | wc -l
63
##on the client
[root@src libexec]# ll | wc -l
64
[root@src ~]# scp /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe root@192.168.56.2://usr/local/nagios/libexec/
The authenticity of host '192.168.56.2 (192.168.56.2)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:A8Z6mVuYWIrJWJkMuDJ7qiGkLHBBWvmcRbMQuoM2ZNM.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:7b:35:06:3e:fe:43:90:7d:c6:a8:0a:00:2c:01:72:b5.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '192.168.56.2' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
root@192.168.56.2's password:
check_nrpe
###Now, it is working on the server on server
[root@emcl libexec]# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 192.168.56.10
NRPE v4.0.2[root@emcl libexec]# cd /usr/local/nagios/etc/
[root@emcl etc]# touch hosts.cfg
[root@emcl etc]# touch services.cfg
[root@emcl etc]# vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/hosts.cfg
cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/services.cfg3. Configuring Nagios Host, Services and command Files
3_1. Configuring Host file
[root@emcl etc]# more /usr/local/nagios/etc/hosts.cfg
## Default Linux Host Template ##
define host{
name linux-box ; Name of this template
use generic-host ; Inherit default values
check_period 24x7
check_interval 5
retry_interval 1
max_check_attempts 10
check_command check-host-alive
notification_period 24x7
notification_interval 30
notification_options d,r
contact_groups admins
register 0 ; DONT REGISTER THIS - ITS A TEMPLATE
}
## Default
define host{
use linux-box ; Inherit default values from a template
host_name src ; The name we're giving to this server
alias Oracle Linux Server release 7.9 ; A longer name for the server
address 192.168.56.10 ; IP address of Remote Linux host
}define service{
use generic-service
host_name src
service_description CPU Load
check_command check_nrpe!check_load
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name src
service_description Total Processes
check_command check_nrpe!check_total_procs
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name src
service_description Current Users
check_command check_nrpe!check_users
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name src
service_description SSH Monitoring
check_command check_nrpe!check_ssh
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name src
service_description FTP Monitoring
check_command check_nrpe!check_ftp
}
# vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/commands.cfg
###add following to the end of the file
define command{
command_name check_nrpe
command_line $USER1$/check_nrpe -H $HOSTADDRESS$ -c $ARG1$
}
[root@emcl etc]# systemctl restart nagios









No comments:
Post a Comment